Signal vs. WhatsApp: Which app offers better privacy

If you’ve ever worried about who can read your messages, you’re not alone. Privacy has become one of the biggest concerns in our digital lives, and choosing the right messaging app is a big part of that. Two of the most popular options, Signal and WhatsApp, both promise end-to-end encryption (E2EE), but they have some important differences under the hood.
In this guide, we’ll take an honest look at WhatsApp and Signal, comparing their privacy, security, business models, and everyday performance to help you choose the secure messaging app that best fits your lifestyle and keeps your private conversations safe.
Signal vs. WhatsApp: Quick overview
Let’s take a closer look at how these two popular apps compare beyond the surface. Signal is a nonprofit project focused on privacy, while WhatsApp is part of Meta’s vast messaging ecosystem. Both promise secure, end-to-end encrypted messaging, but they offer very different user experiences when you dig into their features, data policies, and how they fit into your daily routine.
Signal vs. WhatsApp features
Below is a side-by-side privacy comparison and feature breakdown to help you quickly see how Signal and WhatsApp stack up in terms of what they offer.
| Feature | Signal | |
| Messaging | Text, voice, video | Text, voice, video |
| Group chats | 1,024 members | 1,000 members |
| App lock | ✅ | ✅ (Screen Lock) |
| Notification privacy | Hides message content only | Can hide name, content, and actions |
| Call IP masking | ✅ | ✅ |
| Disappearing messages | ✅ | ✅ |
| E2EE | ✅ | ✅ |
| Data sharing | ✅ (shares data with Meta, parent company) | ❌ (no data sharing; not affiliated with any tech company) |
| Keyboard privacy | ❌ | ✅ (Incognito Keyboard for Android devices) |
| Platforms | iOS, Android, Mac, Windows | iOS, Android, Mac, Windows, Linux |
| 24h (ephemeral) posts | ✅ (Status) | ✅ (stories) |
| Channels (one-way broadcast updates from individuals or organizations) | ✅ | ❌ |
| Polls (simple tool for gathering opinions in group chats) | ✅ | ❌ |
| Editing sent messages | ✅ (up to 15 minutes after sending) | ✅ (up to 10 times within 24 hours of sending) |
| Metadata minimization | ❌ (collects extensive metadata, including your connections, group info, etc.) | ✅ (stores only registration date and last active time) |
| Open source | Partial (the Signal Protocol only) | ✅ (app and protocol are fully open source) |
User base and popularity
WhatsApp is one of the most widely used messaging apps in the world. As of 2025, it has surpassed 3 billion monthly active users, making it an essential communication tool in many parts of the globe. It’s especially popular in countries like India, Brazil, and the United States, where it’s often the default way people stay in touch with family, friends, and even businesses.
Signal, by contrast, has a smaller but highly dedicated user base, with estimates of around 40-70 million monthly active users. It tends to be the app of choice for people who care deeply about privacy, such as journalists, activists, security professionals, or anyone looking for truly private conversations without the data mining. Despite its smaller scale, Signal’s influence is significant: even WhatsApp uses the Signal Protocol for its own encryption.
Supported devices and platforms
Both Signal and WhatsApp support the major platforms, offering solid cross-platform messaging capabilities, but with a few key differences in flexibility and device compatibility.
Signal offers dedicated apps for Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux (64-bit distros with APT like Ubuntu or Debian). However, to use Signal on desktop, you must first set it up on your phone; it won’t work as a standalone app. Signal also supports iPads as linked devices, though Android tablets aren’t currently supported.
WhatsApp is also available on Android and iOS, with support for newer OS versions (Android 5.0+, iOS 15.1+). Like Signal, it requires a phone number and SMS or call access to register. On top of that, WhatsApp supports linking more device types, such as Android tablets, iPads, and even smartwatches (Wear OS). It also has desktop apps for Windows (10 or newer) and macOS (12.1 or newer).
There’s no official WhatsApp client for Linux, though some community-developed workarounds exist. Just keep in mind that unofficial tools may pose security or privacy risks, so use them with caution.
Privacy and security: Who does it better?
Signal was designed from the ground up with privacy in mind. But to be fair, WhatsApp isn’t exactly lagging behind. Over the years, it’s made solid improvements to strengthen instant messaging security, so both apps now have pretty impressive privacy features. Let’s take a closer look at how they compare when it comes to keeping your conversations safe.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE)
Both WhatsApp and Signal offer E2EE by default for all your messages and calls, whether you’re chatting one-on-one or in a group. This means no one else (not even the companies themselves) can read your texts, listen to your calls, or watch your video chats. It’s designed so only you and the person you’re talking to have the keys to unlock your encrypted chats.
Interestingly, both apps actually use the same underlying technology: the Signal Protocol. Signal created this open-source encryption system, and WhatsApp adopted it to secure its own messages. The fact that it’s open source is a big plus for transparency, since anyone can inspect the code to verify that it does exactly what it promises: keep your chats private and secure.
Metadata collection and handling
When you send a message or share media like photos and videos, you’re not just sharing the content itself; you’re also sending metadata. Think of metadata as data about your data. It doesn’t reveal the actual text of your message, but it does offer clues about it, like:
- Who you sent it to
- When it was sent and delivered
- The type of message (text, image, video)
- Its size
- Even your approximate location at the time
It’s a bit like the postage information on a letter. Even if no one can read what’s inside, the address and postmark still reveal a lot.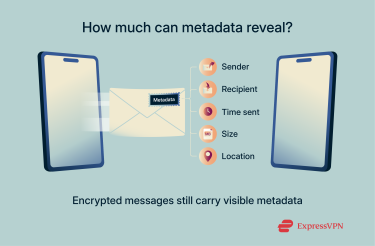 When it comes to metadata privacy, this is where WhatsApp and Signal really part ways.
When it comes to metadata privacy, this is where WhatsApp and Signal really part ways.
WhatsApp uses E2EE to keep your message content safe from prying eyes. But it doesn’t extend the same level of protection to your metadata. It collects quite a bit of usage and log data, like how often you use the app, who you’re in groups with, your profile photo, and even when you’re online or last seen. This kind of metadata can be handed over to law enforcement with the right legal request.
On the other hand, Signal was built with metadata privacy in mind from the start. It collects as little user data as possible. Aside from the date you registered and the last time you used the app, Signal doesn’t keep information about your contacts, groups, or locations.
Even better, Signal developed a feature called sealed sender, which is designed to limit what Signal’s servers can see about who is messaging whom. It doesn’t completely eliminate this metadata, but it reduces the information available to Signal itself. Think of it like sending a letter while trying to keep your return address as hidden as possible. This approach moves Signal closer to its goal of strong metadata privacy, making it harder for anyone (including Signal) to map your communication patterns.
Business model, jurisdiction, and data storage
WhatsApp is part of the Meta family of companies and is based in the U.S. Signal is also U.S.-based, but it’s run by a nonprofit called the Signal Technology Foundation, which is supported by donations rather than ads or tracking.
Because both services are based in the U.S., where certain data retention laws apply, it’s worth asking: what kind of personal data do they collect, and how do they store it?
Signal keeps things minimal. It encrypts your profile picture and name, along with your messages, and only stores the technical data it absolutely needs to function, like authentication tokens and encryption keys.
WhatsApp, on the other hand, collects and stores quite a bit more. It keeps records of groups you’ve joined or created and also gathers other types of metadata, like:
- Your device type and operating system
- Your mobile operator or internet service provider (ISP)
- Language and time zone data
- IP address
- Device battery level and signal strength
- Unique device identifiers
While WhatsApp doesn’t make it clear how all of this data is stored, it’s still significantly more than what Signal collects. Even if some of it is encrypted, that’s a lot of extra information tied to your account.
Third-party data sharing and monetization
WhatsApp is part of the larger Meta family, which also includes Facebook and Instagram. According to its Privacy Policy, WhatsApp shares information with Meta so the parent company can improve its services and offerings. In plain terms, your data helps Meta serve you more targeted ads and content across its platforms.
In other words, your data is used to inform better targeting and content suggestions, among other things.
To be fair, WhatsApp does promise it won’t show you third-party banner ads in the app, at least not for now. But that doesn’t mean your data isn’t being monetized. WhatsApp’s data sharing with Meta means your activity can still influence the ads you see elsewhere in Meta’s ecosystem.
Signal, on the other hand, is basically the opposite. It’s run by a nonprofit foundation that relies on user donations and has no big tech affiliations. That independence helps ensure strong user data protection, since there’s simply no business incentive to share your data with anyone.
Generally, both services need to share some of your data with third-party services, including in cases such as:
- Sending verification codes to your devices
- Collaborating with law enforcement
- Detecting and preventing fraud, security, or technical issues.
In these cases, your data will be subject to the privacy policies of any third-party provider they need to share it with for the intended purpose.
Extra privacy settings
Both WhatsApp and Signal let you tweak your privacy settings, but Signal gives you more tools and more control.
Let’s start with disappearing messages. These are messages that delete themselves after a set time, so they don’t hang around in your chat history forever. Both apps support them, but they work a little differently.
On WhatsApp, the timer starts as soon as the message is sent, meaning it could disappear even if the recipient never opens it. Signal does it better: the timer only starts after the person actually reads the message. That way, you know it was seen before it vanished.
Signal also lets you set much more precise time limits, down to just a few seconds if you want. WhatsApp, in contrast, only gives you three preset options: 24 hours, 7 days, or 90 days.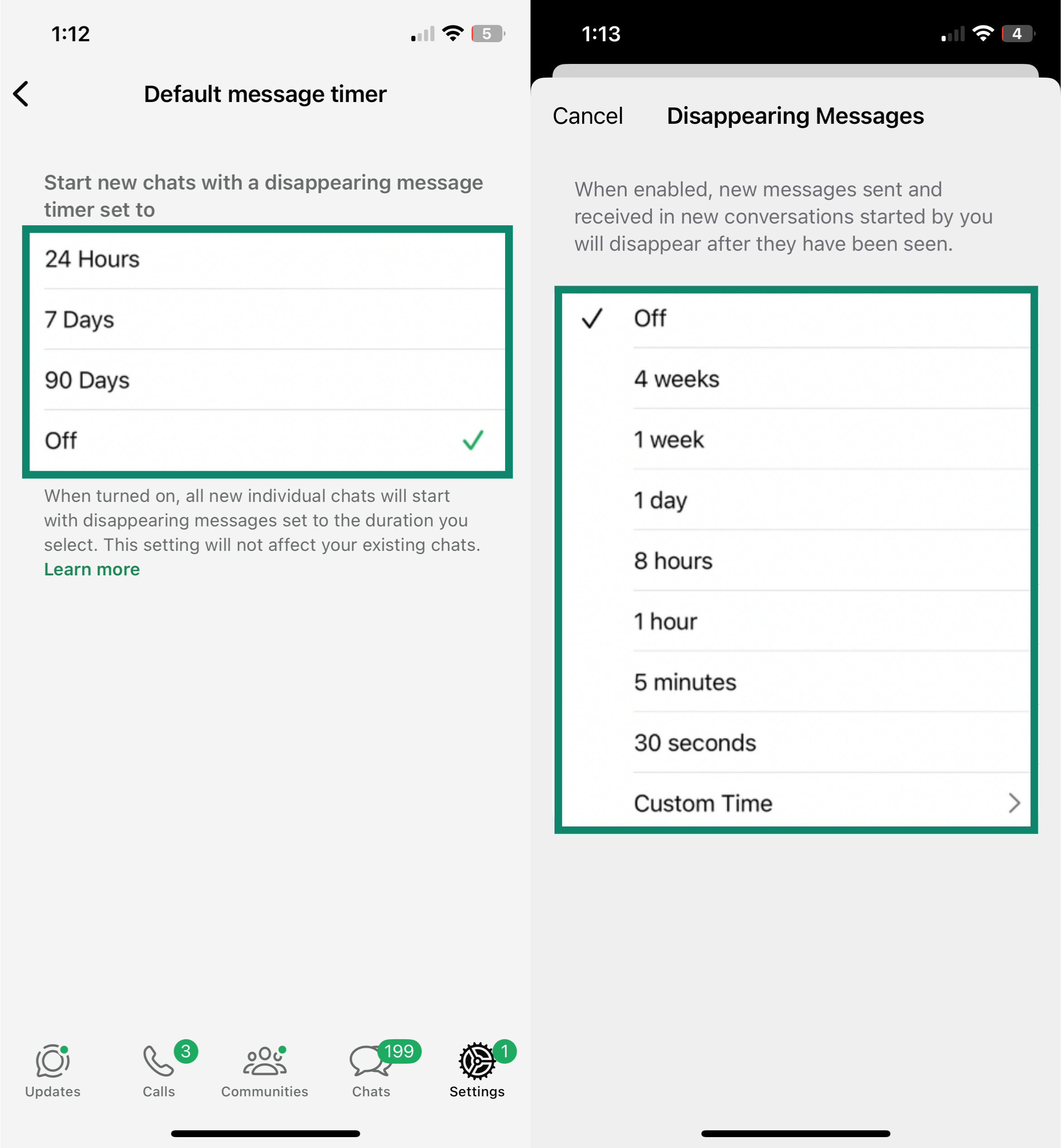 Signal also offers privacy beyond just messages. You can change the app icon in your app drawer, which is handy if you want to make Signal less obvious to anyone snooping through your phone. The app name might still show (depending on your launcher), but it’s a nice layer of discretion that WhatsApp doesn’t offer.
Signal also offers privacy beyond just messages. You can change the app icon in your app drawer, which is handy if you want to make Signal less obvious to anyone snooping through your phone. The app name might still show (depending on your launcher), but it’s a nice layer of discretion that WhatsApp doesn’t offer.
Here are a few other standout Signal privacy features:
- Registration lock: Adds a PIN so no one can re-register your account on another device without it.
- Notification privacy: Lets you hide the sender’s name and message content from push notifications.
- Screen security: Blocks previews of the Signal app when you're switching between apps.
WhatsApp doesn’t offer most of these. The only comparable feature is its version of two-step verification, which works a bit like Signal’s registration lock and is equally important for protecting your account from hijacking.
Learn more: Scams are another risk to watch out for. See our guide to the latest WhatsApp scams and find out how to make your WhatsApp account more secure.
Cloud backups: How private are your conversations?
All your Signal and WhatsApp messages are stored locally on your device. This is crucial to ensure that cybercriminals without access to your physical device can’t simply breach a cloud server to access those messages.
Thankfully, you can also back up your Signal and WhatsApp messages to safely retrieve them on new devices. That said, there are differences to note. For starters, Signal doesn’t allow you to back up your messages to the cloud (Google Drive or iCloud) like WhatsApp does.
Signal does this to ensure your data can never be intercepted in transit or hacked from your cloud storage service. Still, this may be less than ideal for users looking for a reliable way to ensure continued access to messages if their old device is ever lost or damaged. Signal for Android also offers a special local backup feature that prioritizes user data protection. Unlike cloud-based backups that might be accessible to service providers, Signal’s backups are encrypted with a 30-digit passphrase and stored only on your device. You’re in full control; you need to manually move the backup to a new phone if you want to restore it. This approach ensures your encrypted chats stay private, even during device transfers.
Can governments access your chats?
No messaging app can hand over messages encrypted end-to-end, but not all apps treat your surrounding data the same.
In WhatsApp’s case, message content stays private, but other details (like who you talked to and when) can still be shared with authorities if requested. A leaked FBI document in 2021 confirmed that WhatsApp can provide certain metadata to law enforcement almost in real time. The app also offers cloud backups, which are only protected if you’ve manually enabled E2EE.
Signal takes a stricter stance. It doesn’t log your contacts, chat history, or metadata, and has shown in legal requests that it has almost nothing to turn over. The platform was built to store as little information as possible, which leaves little for anyone to access, even under pressure.
Everyday use: Performance and limitations
A good encrypted messaging app should work smoothly no matter what you’re sending or what device you’re on. So how do Signal and WhatsApp compare when it comes to everyday performance?
Messaging, call quality, and media sharing
In terms of messaging and call quality, both apps are solid. You can send texts, images, videos, documents, voice notes, contact cards, and even your live location through either app. WhatsApp has a small edge here, though, as it’s the only one that lets you send polls in both one-on-one and group chats.
File size limits are another key difference. Here's a quick look at how they compare:
| File type | Signal | |
| Image | 16MB | 8MB |
| Video | 16MB | 100MB |
| Document | 2GB | 100MB |
Both Signal and WhatsApp offer strong call quality for voice and video, even on weaker networks. WhatsApp recently introduced the MLow codec, which improves audio clarity, reduces background noise, and boosts reliability on mobile and desktop, even for users with slow connections or older devices.
Signal, meanwhile, uses adaptive jitter buffers and packet loss concealment to keep audio smooth and natural even when packets arrive late or out of order. The tech under the hood is different, but the result is similar: clear, private calls wherever you are.
Syncing across devices
WhatsApp offers true multi-device support. You can link up to four companion devices, such as phones, tablets, desktops, and browsers, to your main account. Each device gets its own encryption keys, and all linked devices stay connected even if your phone is offline, though inactivity beyond 14 days logs them out.
Signal also supports multiple devices. You can link up to five desktop or iPad clients (in addition to your one primary phone). When setting up a new linked device, you can choose whether to transfer chat history (including the last 45 days of messages and media); afterward, they sync seamlessly and remain fully functional, even if your phone is offline.
Accessibility in restricted regions
WhatsApp supports proxy connections, but it doesn’t offer its own proxy servers. Instead, users must manually find or set up a third-party proxy, something that may not be easy or safe depending on their region. Still, this feature helps bypass censorship when direct connections to WhatsApp are blocked. Keep in mind, though, that your IP address is shared with the proxy provider, which may introduce privacy concerns.
Signal previously offered a built-in censorship circumvention tool (domain fronting), which automatically routed traffic through major cloud providers to maintain connectivity in restricted environments. However, this method has largely stopped working after tech giants like Google and Amazon closed those loopholes. Signal now supports connecting via a Transport Layer Security (TLS)-based proxy, which you can set up or find manually, but this isn’t as seamless or resilient as their original solution.
While community-run proxies can sometimes be unreliable, ExpressVPN offers a safer and more stable alternative, giving you an encrypted tunnel to the open internet. It’s easy to use, works on nearly any device, and can automatically adjust your connection to maintain access in restricted environments, all while protecting your real IP address and keeping your traffic private.
Unlike a standalone proxy, a reputable VPN also encrypts all your internet activity, not just your messages, making it a more complete and private solution for staying connected in restrictive environments.
Signal or WhatsApp: Which app fits your needs best?
Now that we’ve looked at both Signal and WhatsApp across privacy, security, features, and performance, the big question remains: which one is right for you? The short answer: it depends on what matters most to you.
Best choice if you prioritize privacy
If you’re looking for a privacy-focused app, Signal is the better choice. Unlike WhatsApp, Signal doesn’t collect message metadata: information like who you messaged, when, how often, and from where. This kind of data may seem harmless, but it can be highly revealing.
It’s also worth noting that Signal created the E2EE protocol WhatsApp now uses. But while WhatsApp is owned by Meta, Signal is run by a non-profit foundation and funded entirely by donations, so it doesn’t rely on your data to make money.
Signal adds extra layers of protection, too. You can hide its content from the app switcher, block screenshots, and even disguise the app icon to make it look like something else, like a weather app. These small touches make Signal one of the most privacy-focused apps in real-world use.
Learn more: Read our explainer to understand how WhatsApp's privacy policy has evolved.
Best option if you need reach and ease of use
If you’re more focused on convenience and reach, WhatsApp wins. With over 3 billion monthly active users, it’s the messaging app almost everyone already uses, from friends and family to small businesses. If you want an app where you don’t need to convince others to join, WhatsApp is the simpler solution.
Learn more: Want to explore other private messaging options? Check out our roundup of the best Signal and WhatsApp alternatives.
FAQ: Common questions about Signal vs. WhatsApp
Is Signal more private than WhatsApp?
Signal is more private than WhatsApp, considering its choice to minimize user data collection, the lack of affiliation to any top tech brands, and a not-for-profit model that ensures it doesn’t need to collect and monetize user data. Signal also offers more data privacy settings than WhatsApp, including the option to disguise the app icon, hide the sender’s name in notifications, and store your backups locally.
Does WhatsApp share my data with Facebook?
Yes. WhatsApp shares certain data with its parent company, Meta. While your messages are end-to-end encrypted, WhatsApp may share metadata such as your phone number, device information, IP address, and usage patterns. This data collection helps Meta deliver services and improve ad targeting across its platforms.
What encryption protocols do WhatsApp and Signal use?
Both WhatsApp and Signal use the Signal Protocol, an open-source end-to-end encryption (E2EE) protocol originally developed by Open Whisper Systems (now the Signal Foundation) in 2013. Signal uses the protocol natively across all communications, while WhatsApp adapted it for its own infrastructure. The open-source nature of the protocol allows for independent audits, which helps build transparency and trust among users.
Can governments access my WhatsApp and Signal chats?
No, governments can’t read your message content on either app because both use end-to-end encryption (E2EE). However, WhatsApp collects and may share metadata (like who you contacted and when) if legally required. Signal, on the other hand, collects almost no metadata, so there’s little it can provide, even under court orders.
How can I migrate from WhatsApp to Signal?
There’s no direct way to transfer your WhatsApp chat history into Signal. While both apps use the Signal Protocol for encryption, their implementations are not compatible, making chat data migration impossible.
However, if there are conversations you want to keep, you can export them from WhatsApp as text files for your own reference, but they won’t appear inside Signal. After installing Signal and registering your number, you can start fresh conversations with your contacts. Signal also lets you easily invite others to join the app.
Which app works better with a VPN: WhatsApp or Signal?
Both WhatsApp and Signal generally work well with a VPN, so performance depends more on your VPN provider than the app itself. However, using Signal with a VPN offers better privacy overall, because while a VPN hides your IP address, it can’t hide the metadata WhatsApp collects. Signal, by design, collects far less metadata.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN