2.4GHz vs. 5GHz: Which Wi-Fi frequency is right for you?

Most modern routers broadcast two signals: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. And if you’ve seen these options pop up on your phone or laptop, you might have wondered, what’s the difference, and does it really matter which one you connect to?
It does, and choosing the right Wi-Fi band can mean the difference between smooth streaming and endless buffering or between lag-free gaming and frustrating disconnects. But it’s not just about speed. The range, the number of devices connected, and even the thickness of your walls all play a part.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi so you can understand which frequency is best for your home, your devices, and your online habits.
2.4GHz vs. 5GHz: What’s the difference?
When you connect to Wi-Fi, you’re not just getting online; you’re choosing between two different radio frequencies: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Both serve the same purpose, but the way they behave in your home can be very different.
The 2.4GHz band has been around the longest. Its lower frequency allows signals to travel further and pass through walls and obstacles with less effort. That makes it useful for devices spread out across multiple rooms or floors. But the trade-off is speed. The 2.4GHz connection is typically slower and more susceptible to interference, especially because so many household devices, like microwaves and baby monitors, use the same frequency.
The 5GHz band delivers faster speeds and handles more data at once. It’s ideal for things like streaming HD videos, playing online games, or joining video calls. However, the higher frequency means the signal doesn’t travel as far and is more easily weakened by walls and physical barriers.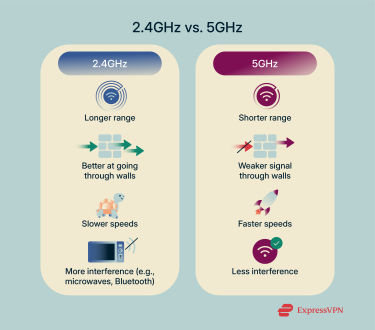
Performance comparison: Speed, range, and interference
The performance of 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi depends on three main factors: how fast the connection is, how far it can reach, and how well it handles interference.
- Speed: 5GHz Wi-Fi offers much higher data speeds than 2.4GHz, thanks to its broader bandwidth. Under optimal conditions, it can exceed 1000Mbps, while 2.4GHz is significantly slower. That’s why 5GHz is better for activities that demand speed, like video calls or large downloads.
- Range: The 2.4GHz band has better range and wall penetration. Its longer wavelength travels further and handles obstacles like walls and floors with less signal loss. 5GHz, with its shorter wavelength, loses strength more quickly when barriers are present. If your device is far from the router or behind several walls, 2.4GHz is more reliable.
- Interference: Many household devices, such as microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and baby monitors, operate on the 2.4GHz band, increasing the likelihood of interference. The 5GHz band, in contrast, is less congested and offers more non-overlapping channels, reducing the chances of signal disruption.
When to use 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz Wi-Fi
As mentioned, most routers today are dual-band, meaning they broadcast both 2.4GHz and 5GHz signals simultaneously. This lets your devices pick the connection that works best in the moment.
Best use cases for 2.4GHz connections
The 2.4GHz band is better suited for situations where distance and obstacles matter more than speed. Its longer wavelength allows the signal to travel further and handle walls, floors, and other barriers with less signal loss.
You’ll get the most from 2.4GHz when:
- Devices are spread out across multiple rooms or floors.
- You need to connect in areas far from the router or where the signal needs to pass through several walls.
- You’re using smart home devices like thermostats, doorbells, or IP cameras, which don’t need high speeds but do need consistent connectivity.
- Simple tasks like checking email, browsing websites, or sending messages are your main activities.
Best use cases for 5GHz connections
5GHz shines when speed is the priority and the devices are close enough to the router to maintain a strong signal. Its wider bandwidth and additional channels make it ideal for handling demanding applications without interference.
You should use 5GHz when:
- Streaming HD or 4K content on TVs, tablets, or laptops.
- Participating in video calls or teleconferences where stability and quality are crucial.
- Playing online games that require low latency and fast data transfer.
- Downloading large files that benefit from higher speeds.
- Your environment has many neighboring Wi-Fi networks, and you want to avoid congestion.
Device compatibility: Phones, TVs, smart devices
Not all devices can connect to both frequencies. Most modern smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and laptops support 5GHz Wi-Fi, especially those manufactured in the last decade. However, older devices, or those designed primarily for low-power tasks, often only support 2.4GHz.
Smart home gadgets, like security cameras and smart plugs, are commonly built for 2.4GHz because it ensures better coverage throughout a home, even with multiple walls in the way.
If you’re unsure, you can check your device’s specifications to confirm which frequencies it supports.
How to check and change your Wi-Fi frequency
Knowing whether your device is connected to 2.4GHz or 5GHz Wi-Fi can help you troubleshoot connectivity issues or optimize your internet experience. Switching between these bands is a simple process that usually involves your router’s settings or your device’s network preferences. Here’s how to check your current Wi-Fi frequency and how to change it if needed.
How to tell if your Wi-Fi is using 2.4GHz or 5GHz
The easiest way to know which frequency your device is using is to check the network name or your device’s connection details. Many routers label the SSID (the network name) to indicate the frequency, such as “HomeWiFi_2.4G” or “HomeWiFi_5G.” If your network names don’t specify this, you can check directly on your device.
On Windows
Follow these steps on Windows:
- Click on your Wi-Fi icon and find your network.
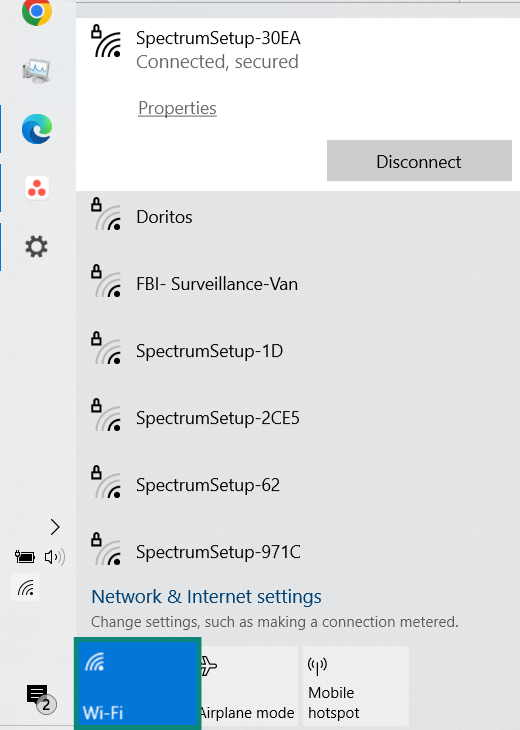
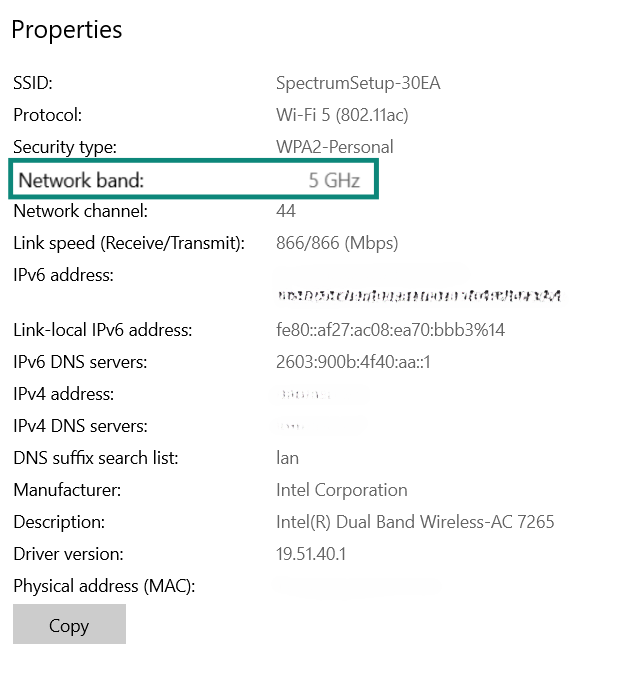
- Click Properties. Scroll down through your network details until you find your network band.
On Mac
On Mac, hold the Option/Alt key and click the Wi-Fi icon on the menu bar. A pop-up will show the connection details, including the channel number, which can indicate if you’re on 2.4GHz or 5GHz.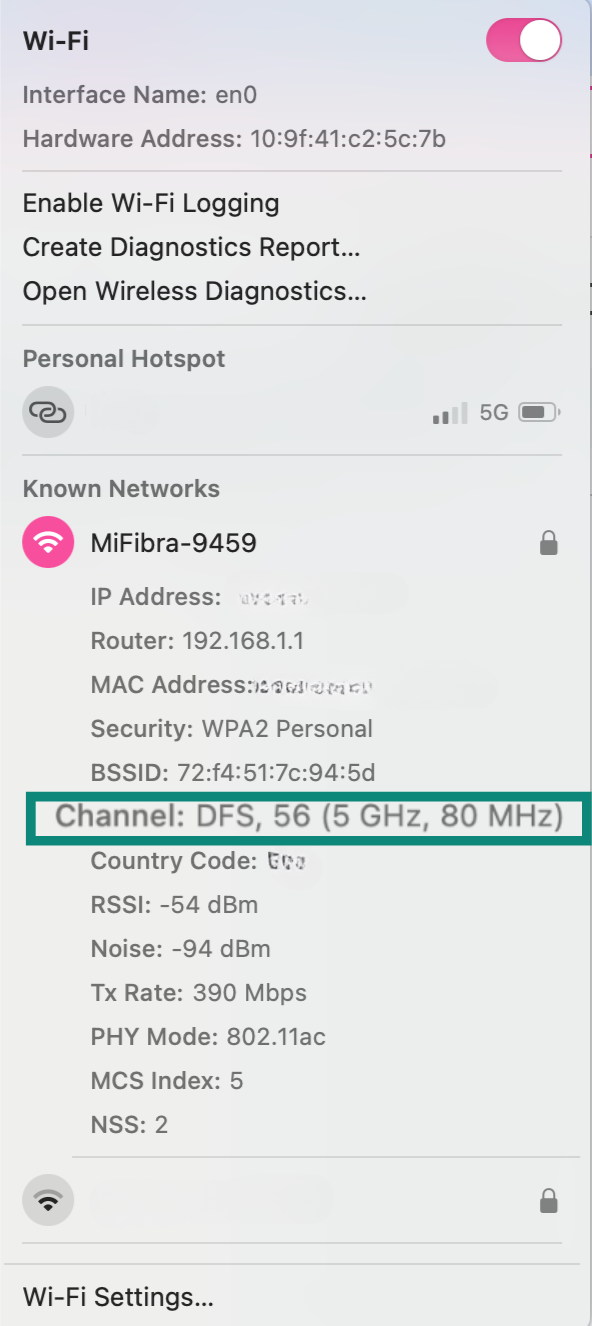
How to switch between 2.4GHz and 5GHz on your router
If you want to change your Wi-Fi frequency, you’ll need to access your router’s settings. The steps are generally similar across routers, but the exact menus might differ depending on the brand and model.
Either way, you first need to find your router’s IP address (on most devices, the default IP address is 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.)
Finding your router’s IP address on Windows
-
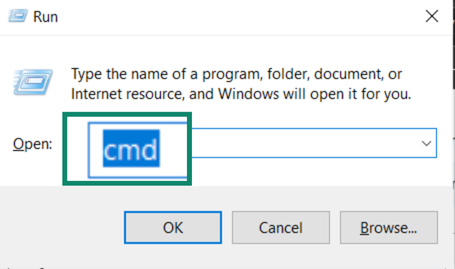
- On Windows, press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter.
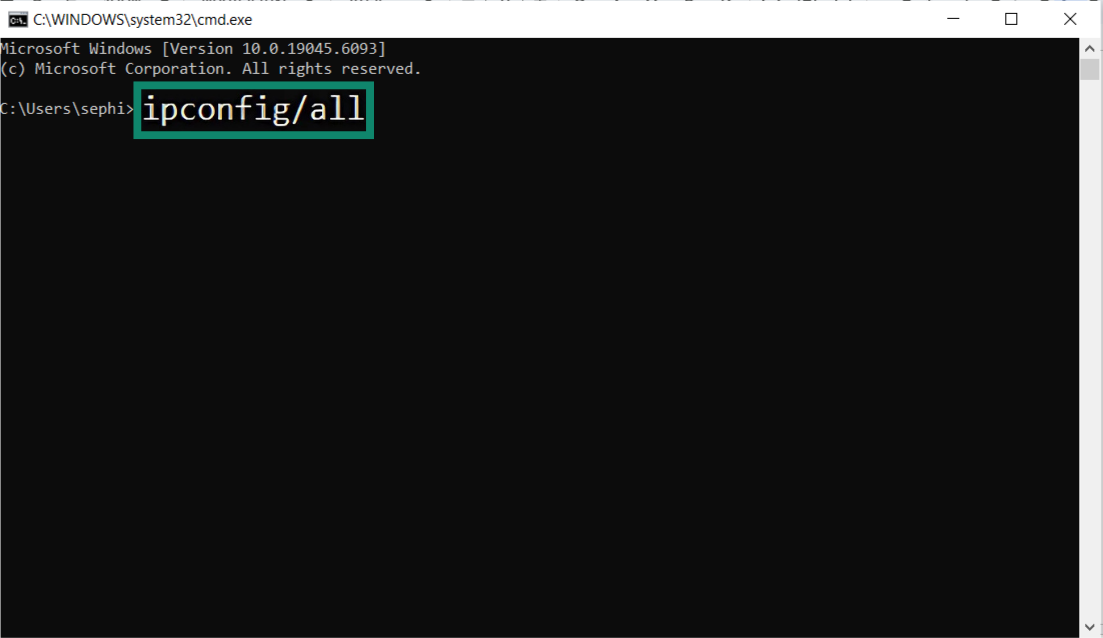
- Type ipconfig /all.
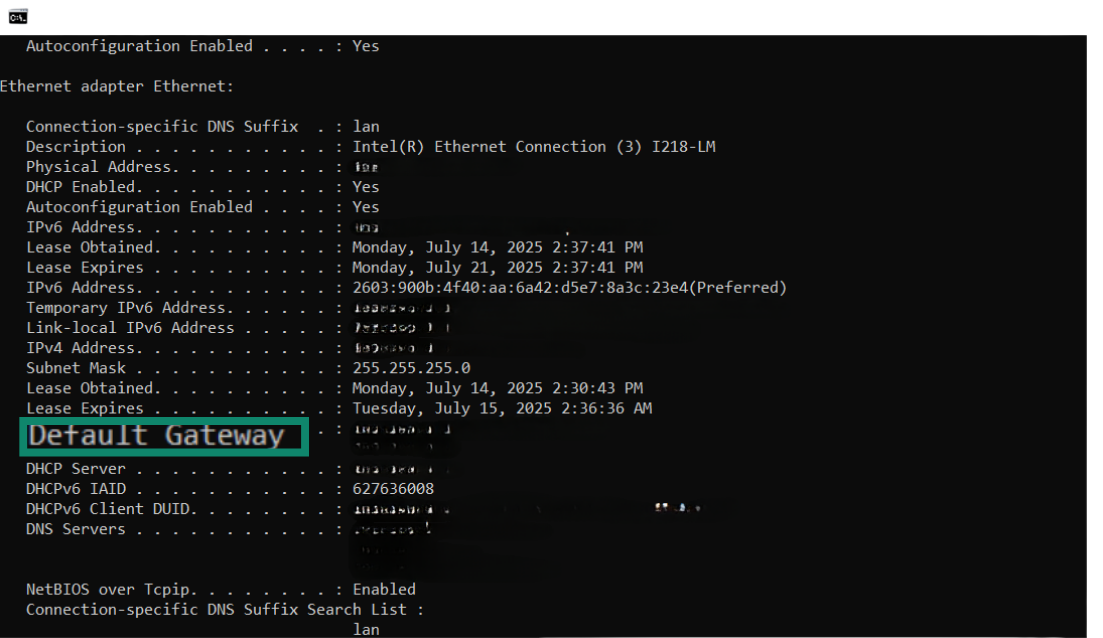
- The Default Gateway is your router’s IP.
- On Windows, press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter.
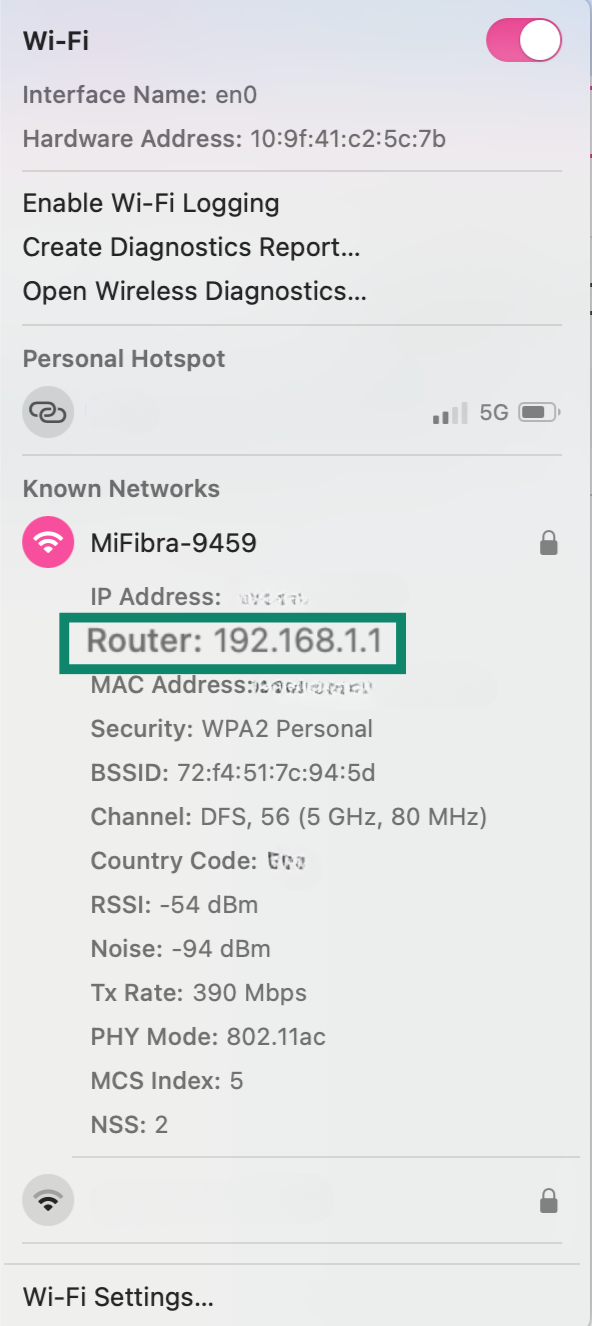
Finding your router’s IP address on Mac
Hold the Option/Alt key, click the Wi-Fi icon, and look for the Router address.
Switching between frequencies
To switch between 2.4GHz and 5GHz on your Wi-Fi network, the process is the same whether you’re using Windows or Mac. Once you have your router’s IP address, you can adjust the settings from any browser or, if your provider offers an app, directly from there.
These steps were completed using the Spectrum router app, but menus and options may look different depending on your router model or provider.
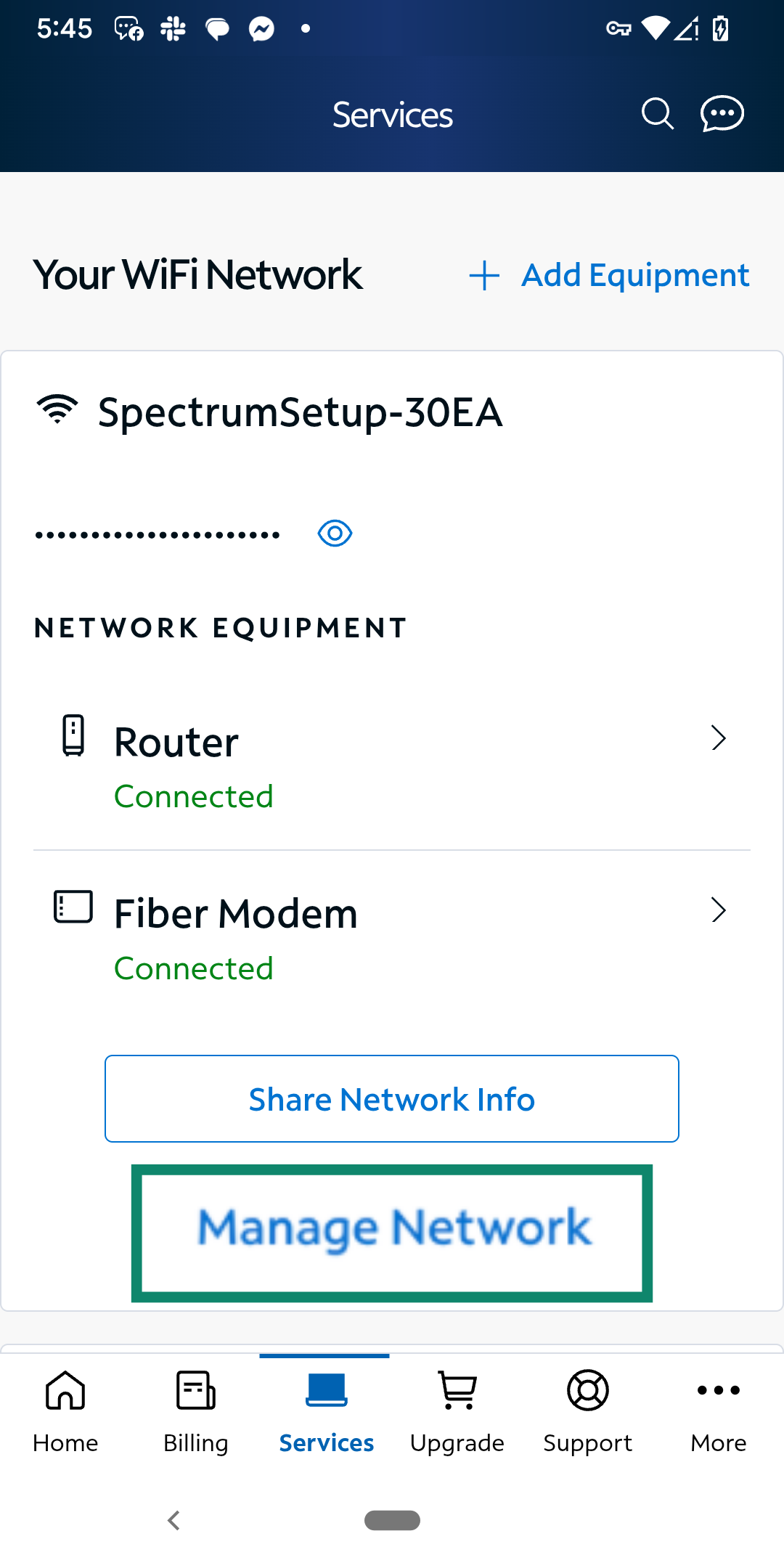
- Access your router settings. Open the Spectrum app on your smartphone and go to the Services tab. You’ll see your Wi-Fi network details, including your connected router and modem. Tap Manage Network to start.
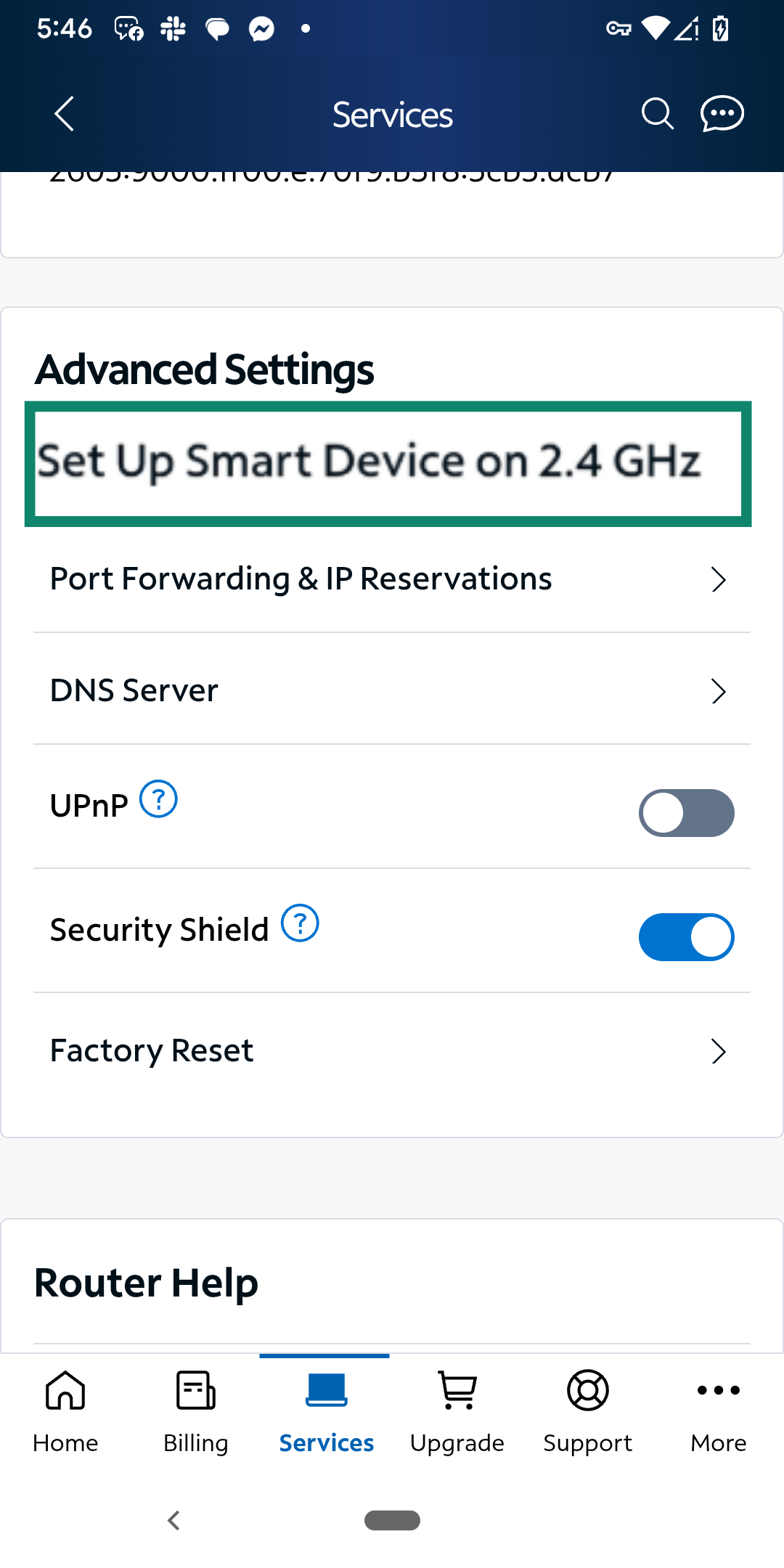
- In the Advanced Settings section, look for the option Set Up Smart Device on 2.4GHz. This allows you to temporarily switch your network to 2.4GHz, which is useful when setting up smart devices that don’t support 5GHz.
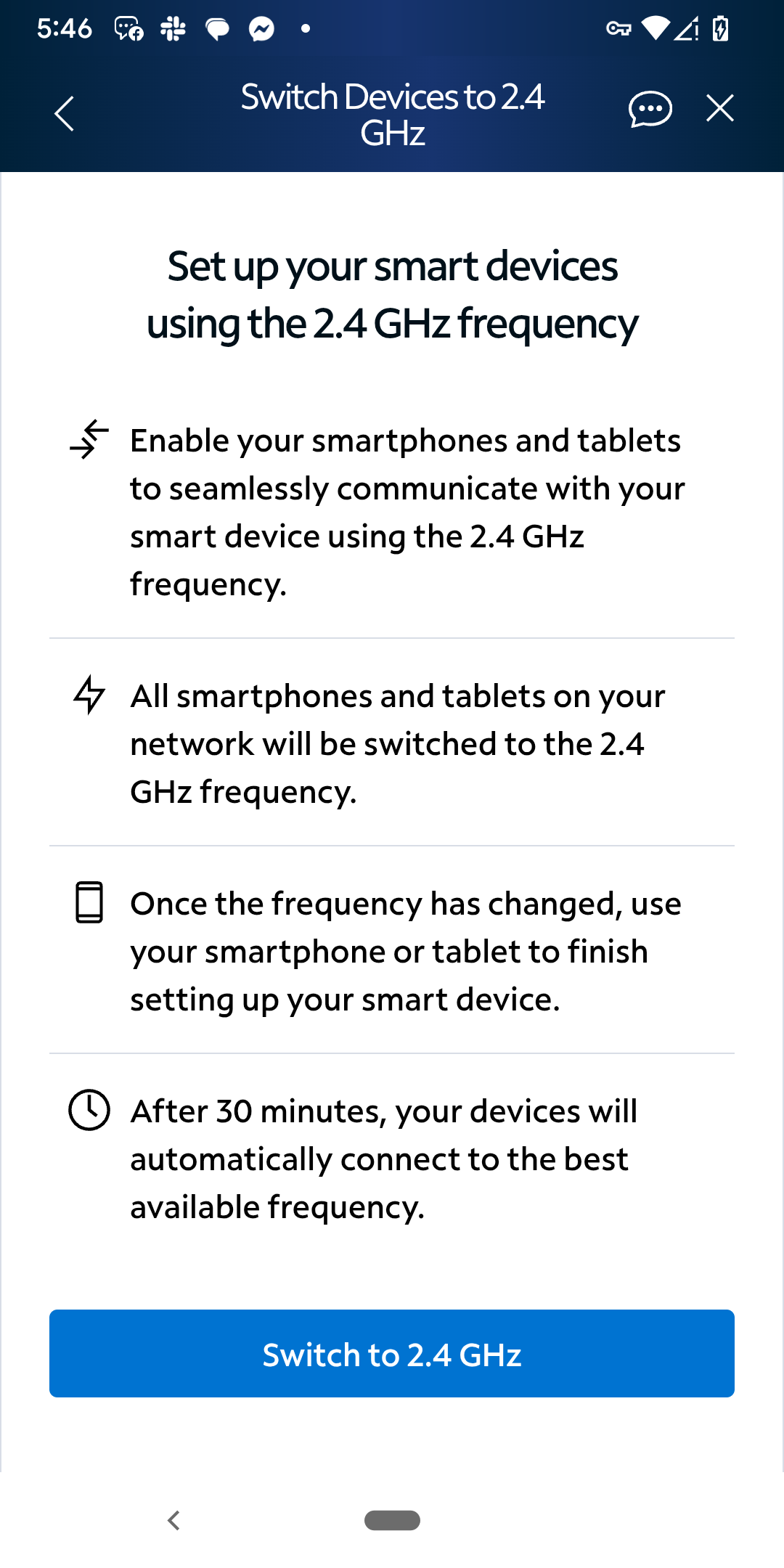
- Tap Switch to 2.4GHz and follow the instructions. Your network will remain on 2.4GHz for 30 minutes, giving you time to set up your device. After that, the router automatically returns to the best available frequency.
These steps let you control which frequency your router uses and can help ensure your devices connect to the band that best suits your needs, whether that’s greater range with 2.4GHz or faster speeds with 5GHz.
What about dual-band, tri-band, and Wi-Fi 6/7?
Modern routers aren’t limited to just one frequency band. If you’ve ever noticed multiple Wi-Fi networks with similar names in your home, chances are you’re already seeing dual-band or tri-band technology in action.
These advanced routers are designed to handle more devices and deliver better performance, especially when combined with newer Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7.
How dual-band routers manage both frequencies
Dual-band routers broadcast both 2.4GHz and 5GHz signals simultaneously. This allows devices to connect to the most appropriate band based on their capabilities and distance from the router.
Some routers include features like band steering, which automatically guides devices to the optimal frequency without requiring users to switch manually. This helps balance network traffic and ensures devices stay connected on the best possible band.
What tri-band and Wi-Fi 6/7 bring to the table
Tri-band routers add a third signal, usually a second 5GHz band or a 6GHz band in newer models. This extra band helps spread traffic across more channels, reducing congestion when multiple devices are connected. It’s particularly useful in households where many users are streaming, gaming, or making video calls at the same time.
These standards are built to handle dense networks filled with smart devices, offering better performance even when many connections are active. They also improve battery life for connected devices thanks to more efficient data handling.
Altogether, dual-band, tri-band, and the latest Wi-Fi versions work together to provide faster, more reliable connections across a wide range of devices and home setups. If you’re looking for a router built with these advanced features and optimized for privacy, ExpressVPN’s Aircove router is a great Wi-Fi 6 option that also has a portable version.
Final thoughts: Choosing the right frequency for your needs
There’s no single frequency that works best for everything. It really depends on your space, your devices, and how you use the internet. If you want your connection to reach further, through walls or into distant rooms, 2.4GHz is usually more reliable. For higher speeds when you’re close to the router, especially for streaming or gaming, 5GHz makes more sense.
A dual-band or tri-band router can simplify things by handling multiple bands at once, so each device connects where it performs best. That way, you don’t have to choose just one frequency as your network adapts to what you need. And if Wi-Fi still doesn’t deliver the stability you want, you might want to explore using a wired connection. Learn more about Ethernet vs. Wi-Fi here.
FAQ: Common questions about 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz
Is it better to connect to 5GHz or 2.4GHz?
It depends on your priorities. 5GHz offers faster speeds and is ideal for activities like streaming or gaming if you’re close to the router. 2.4GHz provides wider coverage and better signal through walls, making it better for devices farther away or in different rooms.
Does 5GHz Wi-Fi go through walls?
5GHz WiFi can go through walls, but the signal weakens significantly with each obstacle. Its shorter wavelength is more easily absorbed or reflected by walls compared to 2.4GHz, which retains a stronger signal over distance and through barriers.
How do I know if my Wi-Fi is 2.4GHz?
You can check your Wi-Fi frequency in your device’s network settings. You can find step-by-step guides for both Windows and macOS here.
Alternatively, your router’s admin panel lists the connected devices and their frequency band.
Should a smart TV be on 2.4GHz or 5GHz?
For the best connection quality, it’s recommended to connect your smart TV to the 5GHz band if available. This frequency faces less interference from other household devices compared to 2.4GHz, reducing the risk of slower speeds and buffering during streaming.
Can I use both 2.4GHz and 5GHz at the same time?
Yes, if your router is dual-band, it broadcasts both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies simultaneously. This allows your devices to connect to the most suitable band depending on their capabilities and distance from the router. Some routers even have a feature called band steering, which automatically guides devices to the optimal frequency to balance speed and coverage.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN